Day 1 :
- Nursing Education | Nursing Practice and Research | Types of Nursing | Healthcare and Management | Midwifery and Women Health Nursing | Nursing Leadership and Management | Family Nursing | Clinical Nursing and Practice | Cancer Nursing | Pediatric Nursing | Surgical Nursing | Adult Health Nursing | Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing | Critical Care and Emergency Nursing | Neonatal Nursing and Maternal Healthcare | Heart and Cardiovascular Nursing | Gynaecology and Obstetrics Nursing
Session Introduction
Kalpana Paudel
Tribhuvan University, India
Title: Exploring the Caring Incorporating Yoga Program in Promoting Physical Recovery of Stroke Patients in Acute Phase

Biography:
Kalpana Paudel working in the Department of Adult Nursing, Maharajgunj Nursing, Institute of Medicine, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal. Her research mainly focuses on acute stroke, caring, physical recovery, yoga.
Abstract:
Background. Currently, caring science integrating cultural practices become an important health resources to get positive health outcomes for hospitalized acute ill patients. Yoga, a cultural practice, has power to bring multiple physical improvements among strokes. However, there is dearth of study on application of caring incorporating yoga for promoting physical recovery among stroke patients particular in the acute phase. Purpose. The study aimed to analyze the experiences of the participants (nurses, patients and family members) focusing on their roles and perceived perception of power of caring incorporating yoga to promote physical recovery among stroke patients during the acute phase. Design. The study is a part of an action research entitled "Development of a Caring Model Incorporating Yoga for Promoting Physical Recovery and Wisdom of People Living With Stroke". Methods. Semi-structured interviews were conducted to collect data in a university hospital, Nepal. An inductive content analysis approach was used for data analysis. Findings. The emerged themes from qualitative data were 1) caring as a tool to enhance trusted relationship, and capacity of stroke during acute phase; 2) yoga as a practical and powerful tool for physical recovery of stroke during acute phase: and 3) perceived physical recovery as a result of the caring incorporating yoga intervention. Conclusion. Physical recovery was successfully achieved by the application of caring incorporating yoga among stroke patients in the acute phase. Clinical Relevance. This study suggests that nurses can successfully facilitate early physical recovery of stroke patients using yoga during their acute phase. While yoga is well accepted by the Hindu stroke patients as it is culturally congruent with their sociocultural background and effective for physical recovery and healing the whole person.
Key Words. acute stroke, caring, physical recovery, yoga,
Salpy Akaragian
Emeritus UCLA Health, Director of Nurse Credentialing & International Nursing, USA
Title: The Prevalence of High Blood Pressure in Armenians

Biography:
Dr. Salpy Akaragian retired from UCLA Health after 44 years of service. She held positions from staff nurse to administrator. Currently, she consultants to health care organizations in Armenia.
Salpy served on the California Board of Registered Nursing and was the US Partner Representative for USAID/AIHA grants. She founded and was the first president of the Armenian-American Nurses Association and formed the Nurses Association in Armenia. She is the Founder and President of Armenian International Medical Fund in the US and Armenia.
Salpy received a Bachelor and Master of Science, and Doctorate of Philosophy degrees from UCLA School of Nursing.
Abstract:
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in Armenia (World Health Rankings, 2012). Limited data exists on the prevalence of risk factors and other contributors to the development of CVD. Understanding the prevalence of various risk factors is a critical first step towards addressing the burden of disease among any population.
Materials and Methods
This descriptive, cross-sectional study examined the prevalence of HBP and risk factors associated with HBP in a select group of Armenian men and women ages 21 and older, living in Armenia. The study followed Joint National Committee-8 guidelines to collect BP data and was conducted at a single point in one clinic.
Results
The convenience sample was composed predominantly of middle-aged females, married, and had a high school education or higher. Over half of the adults of the sample were prehypertensive or hypertensive. Over three-quarters of the participants never smoked and over half of the respondents consumed alcohol in the past 12 months. The nonparametric Spearman correlations indicated that BP level had significant moderate to large correlations with many factors. The results of the stepwise multiple regression model indicated that BP levels were higher with greater waist circumference, a personal history of HBP, high total cholesterol, being male and older age. Furthermore, a fraction of hypertensive respondents had their HBP controlled and more than half of the respondents scored low on MMAS-8 scale.
Conclusion
The findings of this study about the associations between HBP and waist-hip ratio, age, BMI, Total-C, low HDL-C, and high LDL-C were consistent with past research. Waist circumference was the strongest predictor of HBP. The findings of the study cannot be generalized, it must be duplicated by increasing sample size in Yerevan and for the other 10 regions in Armenia.
Peter Mouritzen
Samplix ApS, Denmark
Title: Xdropâ„¢ - Targeted sequencing enabled into the dark and unknown

Biography:
With more than 20 years of experience in the life science industry, Peter is heading market and application development at Samplix. Here efforts are currently focused on the recently launched Xdrop™ technology which introduces an entirely new concept for target enrichment for both short and long read sequencing. Prior to joining Samplix Peter was Global Head of
Abstract:
Targeted sequencing data will never be better than the input material generated during the targeted enrichment process! While this may seem trivial, very few targeted enrichment technologies allow maintaining the integrity and quality of the DNA during enrichment. This results in both false positives and false negative results and can significantly impact conclusions. The Xdrop™ innovation, a novel robotized microfluidics-based focused on advancement framework, empowers quick focused on improvement while keeping up the nature of the DNA and subsequently makes it conceivable to dodge the ancient rarities presented with other enhancement advances. Here we show the Xdrop™ framework being utilized to succession incorporated infections and their encompassing obscure chromosomal grouping, long GC rehashes, and we show staging of malignant growth changes from sub-nanograms of DNA. Districts of 40-70 kb are enhanced and sequenced utilizing Illumina, PacBio, and Oxford Nanopore sequencing at high inclusion. Apart from the Xdrop™ reagents, just 0.2-10 ng of input DNA and two adjacent 20-25 bp primers are used for the enrichment of a chromosomal region and it is therefore fast and easy to set up for a new region. The primers are located in the central part of the enriched region which means that partially unknown regions can also be enriched using the system making it relevant for regions with structural variation, CRISPR gene editing, gap closing, variable viruses or bacteria, pseudogenes etc. We also show that the Xdrop™ system can be used for general, unbiased isothermal amplification of small amounts of samples of DNA for any type of downstream sequencing.
Lyne Chamberlain
Nursing in Central Florida’s Seminole State College’s, USA
Title: Perceived Social Support and Self-Care in Hospitalized Heart Failure Patients

Biography:
Lyne Chamberlain was a Clinical Nurse Specialist with expertise in chronic heart failure patients and a passion for facilitating self-care when this study was conceived. She has presented at numerous national conventions for the American Association of Heart Failure Nurses and the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses. Lyne has also published several articles related to heart failure self-care. Currently Dr. Chamberlain is the Program Manager and a Professor of Nursing in Central Florida’s Seminole State College’s bachelors program.
Abstract:
Statement of Problem: Self-care is recommended in heart failure (HF) management and to reduce hospitalizations, yet only one study has demonstrated improved patient outcomes with adequate self-care. This study evaluated perceived social support and self-care in hospitalized HF patients compared with community dwelling HF patients.
Methodology and Theoretical Orientation: The medical outcomes study of social support (MOS-SS) and the self-care of heart failure index (SCHFI) were the key measurement instruments for this multisite descriptive study. Multiple regression and two-sample t tests for unequal variances were used to analyze the data from a convenience sample of 121 hospitalized HF patients and a comparative study of 211 community-dwelling HF patients. Theoretical frameworks were the Self-Care of HF Theory and the Stress-Buffering Model of the Social Support Theory.
Findings: Hospitalized HF patients had significantly lower self-care maintenance scores and perceived social support than community-dwelling HF patients. Perceived social support was associated only with self-care confidence, and self-care confidence was associated with self-care maintenance and self-care management. 25% of hospitalized study candidates had cognitive impairment compared with less than 6% of community-dwelling patients.
Conclusion and Significance: Community-dwelling HF patients had better self-care skills than hospitalized HF patients. Additional research is needed to determine the best strategies for improving self-care or reasonable substitutes in these patients. Additional research is also needed to evaluate cognitive impairment across the spectrum of HF patients, as this impairs self-care success.
Marcela Ižová
Catholic University in Ružomberok, Slovakia
Title: Falls as an extraordinary event in health care facilities

Biography:
Marcela Ižová has sucessfully completed her PhD at the age of 33 years at Trnava University in Trnava, Slovak republic. She finished specialized studies in nursing care in the field of internal medicine in 2010 and also completed specialized studies in health management and financing specialization in 2014. She is a member of professional organization of Slovak Chamber of Nurses and Midwives in Slovakia.
Abstract:
Introduction: Patient`s falls are often due to misconduct by healthcare professionals, inappropriate risk assessment or misdiagnosis. Number of falls is one of the quality indicators provided by nursing care. Slovak researchers together with French colleagues found out that falls were the second most undesirable events in health care. The purpose of our study is to describe the falls and its prevention in healthcare facilities. Methodology: The study used a questionnaire as a data collection method. The results are evaluated in the form of absolute and relative abundance. For the purposes of analysis we used a chi-squared test. The results were interpreted at the significance level α=0.05. Results and discussion: results of analysis (p=0.00) indicates that nurses use an interview with a patient and a family members in determining the risk of fall. These results were at statistically higher levels. The result of analysis (p=0.00) in a different scenario indicates that there is a dependency between departments and education about factors that increase risk of falling. Accident and emergency nurses provide education at significantly higher rate than nurses in other departments. Nurses indicate that the most common cause of falls was slippage. The results of analysis (p=0.02) showed that there is a statistically significant difference in the approach nurses report a fall report on individual departments. Respondents in all departments apart from internal department report a fall to a doctor. Conclusion: Identification of a risk patient should be considered a key concern in prevention of falls and in planning patient`s care.
Petra Králová
Palacky University Olomouc, Czech Republic
Title: Validation of tool for evaluating the quality of working life - ProQOL – for use in an international descriptive study of post-communist countries in Central Europe

Biography:
Petra Králová is student of PhD at the Palacky University in Olomouc. She works as a healthcare reporting specialist in the DRG system at the Institute of Health Information and Statistics of the Czech Republic and as an assistant professor at the Institute of Nursing Theory and Practice of the First Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univesrity in Prague. She publishes mostly in a field of nursing and health economics.
Abstract:
Interest in the issue of nursing job satisfaction in post-communist countries is related to the socio-political aspects with which these European countries are currently confronted, which are intensified by the acute shortage of nurses due to repeated structural changes in health care, demographic unfavorable situations and high fluctuations. According to The European NEXT-Study conducted in ten European countries, nurses in former post-communist countries report the lowest work satisfaction and worse physical and mental health. In these countries a lot of attention is being given to surveys about factors affecting the satisfaction of nurses, but the quality of working life is being investigated limited only. One of the commonly used tools for measuring work quality of life is the Professional Quality of Life (ProQOL) questionnaire. Questionnaire evaluates the quality of working life based on the assessment of aspects of positive feelings experienced by helping others, which is called Compassion Satisfaction and aspects of negative feelings called Compassion Fatigue, which indicates exhaustion based on a great emotional bond to patients and their families. Because the questionnaire is not linguistically and statistically validated in some Central European countries, comparisons with research conducted in other countries are not possible. The aim is to linguistically validate the Czech and Slovak versions of the ProQOL questionnaire, which will be subjected to a psychometric analysis by a group of respondents. The ProQOL questionnaire will be translated using the "Translation/Back Translation" and "Focus Group Translation" methods. After the translation, a pre-test will be conducted in the form of cognitive interviews to assess the formulation and the understandability of items. Subsequently, the assessment of concurrent and content validity will be carried out with bilingual healthcare respondents. At last, reliability and constructive validity will be evaluated. Because "quality of life" is an abstract criterion, factor analysis will be needed for validation purposes. If the results of validation and subsequent psychometric analysis reach the desired values, the questionnaire can be used to investigate large populations and international comparison of the observed results.
Priyanka Dhiraj Salve
Maharashtra Institute of Mental Health, Center of Excellence, Pune
Title: Drug compliance and psychiatric patients

Biography:
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: “A Study To Assess The Effectiveness Of Self Instructional Module (Sim) On Knowledge And Attitude Of Medication Compliance Among The Care Takers Of Mentally Ill Patients In Selected Mental Hospitals”.
World Health organizes the importance of psychological well- being, defines “health is the state of complete physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”
According to World Health Organization, Mental Health includes “Subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence and self-actualization of one’s intellectual and emotional potential, among others”.
OBJECTIVE
1) To assess the Level of knowledge regarding medication compliances among care takers of mental ill patients in selected Mental Hospital, Pune.
2) To assess the attitude of medication compliance among care takers of mentally ill patients in selected Mental Hospital, Pune.
3) To assess the effectiveness of Self Instructional Module (SIM) on knowledge and attitude regarding medication compliance among care takers of mentally ill patients in selected mental hospital, Pune.
4) To find the association with study finding and selected demographic variables
Conclusion & Significance: Following study can be undertaken in relation to present study.
• A similar study may be replicated on large samples; there by findings can be generalized.
• The study can be undertaken in different settings and different target population such as identical samples.
• A comparative study can be done to assess effectiveness of two different self instructional modules.
Image
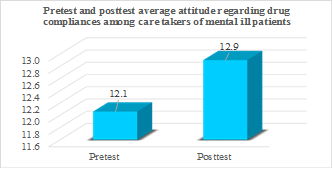
Bar diagram showing effectiveness of Self Instructional Module (SIM) on attitude regarding drug compliance among care takers of mentally ill patients
Bonnez Yannic
Artesis Plantijn University College, Belgium
Title: Vital signs, the magic key in preventing hospitalization and death of older adults living in nursing homes?

Biography:
Yannic Bonnez completed his master of Nursing and Midwifery in 2013, while working at a geriatric ward and the Artesis Plantijn University College (Antwerp). The past years, he taught at the University College, especially at the domain of research and geriatrics. At the same time, he cooperated at different scientific studies.
Abstract:
Background
Yearly, 10% of older adults living in nursing homes (NH) are hospitalized. The goal is to study the relation between (changing) vital parameters and negative health outcomes, and to develop an instrument able to detect early signs potentially giving rise to physical decline.
Method
Weekly assessing vital signs in 170 NH residents (≥65years) during 8 weeks. Medical records were consulted for the Katz-scores and registration of hospitalizations. This abstract was based on preliminary baseline data.
Results
10% of residents were hospitalized and 3% died during follow up (n=170). A significant positive correlation was found between heart ritme (HR) and hospitalization(r=0,152;p<0,05), HR and death(r=0,214;p<0,05) and a significant negative(moderate) correlation between saturation and death(r=-0,353;p<0,001). Those who were hospitalized had a significantly higher HR(p<0,05). A lower HR was found in the survivor group vs those who died(p<0.05).
Discussion
Literature supports the hospitalization percentage(10%) and confirms that higher HR gives rise to elevated risk for hospitalization and death. However, this has mainly been studied in people with increased cardiovascular risk in hospitals. Limitations of the current study are a small sample size and possible confounders (eg infection without hospitalization).
Conclusion
HR positively correlates with hospitalization and death in persons living in NH. A negative correlation was found for saturation and death. A significantly higher HR was found in those who died or were hospitalized. Expansion of the cohort and further research on the optimization of a screening tool is foreseen within this project in order to make more profound pronouncements on the topic.
Dale M. Hilty
Mount Carmel College of Nursing, USA
Title: Using Interdisciplinary Teaching to Illustrate the Relationship between Nursing Specialties & Statistics

Biography:
Dale M. Hilty received his PhD in counseling psychology from The Ohio State University Department of Psychology. He has published studies in the areas of psychology, sociology, and religion. Between April 2017 and April 2018, his ten research teams published 55 posters at local, state, regional, national, and international nursing conferences. His colleagues sharing the author line of this poster are: Ann Waterman, PhD, RN; Bev Gish, MS, RN; Jody Gill-Rocha, MS, RN; Erin Dougherty, MSN, RN, Kerry Fankhauser, DNP Candidate, MS, RN; Mary Yoder, MS, RN; Patty Severt, MSN.
Abstract:
Purpose & Research Question/Hypotheses:
It is hypothesized that interdisciplinary team-teaching with cognitive-affective strategy would increase student engagement by demonstrating relationship between nursing specialties and statistics.
Theoretical Framework & Rationale:
Many students come to college with rudimentary understanding of statistical principals. Students report high levels of motivation and self-efficacy for nursing courses, and low levels of motivation and self-efficacy for the statistics course based on past beliefs, attitudes, and experiences. They also lack the critical thinking skills necessary to apply statistical principles in order to understand the profound impact of evidence in nursing. This difficulty is compounded by their apparent lack of passion about statistics, resulting in an inability for the knowledge to take root.
Method:
The Health Statistics is designed to introduce the nursing students to statistics. Seven nurse faculty offer 20-minute presentation in their area of expertise (e.g., angina, hypertension). Statistics faculty provide a 10-minute demonstration converting nursing constructs to nursing research variables with hypothetical-fictional data based on published findings. Students received a graded worksheet assignment and interpreted the SPSS findings based on ANOVA and linear regression.
Results:
First, pre-post (five knowledge/comprehension questions) data showed significance (p=.001-.031) using dependent t-test. Second, qualitative theme analysis reported students found meaning, relevancy to nursing practice. Third, thirty students volunteered to design and implement research projects not for class/grade for the purposes of developing a professional poster. Four, the interdisciplinary team reported experiential learning while designing the guiding worksheet questions which students applied to patient care and self-care.
Dale M. Hilty
Mount Carmel College of Nursing, USA
Title: Qualitative & Quantitative Analyses of Nursing Panel Teaching Strategy for Non-Nursing Courses

Biography:
Dale M. Hilty, Associate Professor, received his PhD in counseling psychology from The Ohio State University Department of Psychology. He has published studies in the areas of psychology, sociology, and religion. Between April 2017 and April 2018, his ten research teams published 55 posters at local, state, regional, national, and international nursing conferences. His colleague sharing the author line of this poster are: Ann Waterman, PhD, RN. Dr. Waterman is the Interim Academic Dean at Mt. Carmel College of Nursing. She has a BSN from Capital University, & MSN and PhD from The Ohio State University.
Abstract:
Introduction:
In four-year baccalaureate programs, nursing students begin actual nursing courses in the second year. Since most beginning nursing students are developing an authentic perception of a nurse, students are highly motivated and enthusiastic about the nursing panel (NP) experience. The NP consists of seasoned nursing faculty members, and is used to socialize these beginning nursing students into the profession of nursing.
Method:
NP experience lasts 90 minutes. First, the NP members introduce themselves and share their nursing background. Second, students ask questions. In the last 5 years approximately 400 students have been participants. This innovative, interdisciplinary teaching approach assists students in developing authentic nursing knowledge and perceptions. Examples of strategies: nursing faculty on the panel being oriented to the content in the non-nursing class, a caring and respectful educational environment, students come prepared with questions, and all faculty engage in the discussions.
Qualitative Findings
The outcomes: Enhanced learning, positive student evaluations, awareness of the role of the nurse, reciprocal connections, student and faculty satisfaction, increased knowledge of the profession of nursing, nurse self-concept images, and nursing values (trust, caring, unconditional positive regard). These outcomes were derived from student evaluations and reflection papers.
Quantitative Findings
Calling & Vocation Questionnaire (CVQ) was used to assess the presence of, and search for, a calling. CVQ exploratory factor analysis revealed six reliable common factors (subscales) forming CVQ-Presence and CVQ-Search scores. CVQ items provided pre-/post-test evaluating the NP. Using SPSS 25, dependent t-test analyses found significance (p=.001-.042) on all CVQ common factors.
